Mycosphaerella Caricae
Annular Spot of Papaya / Mycosphaerella Caricae.
The papaya annular spot is caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella caricae , this disease is widely distributed, and is undoubtedly one of the most common diseases of this crop
Symptom.
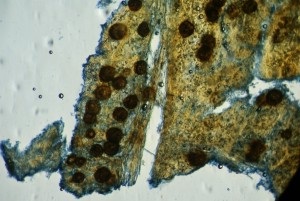
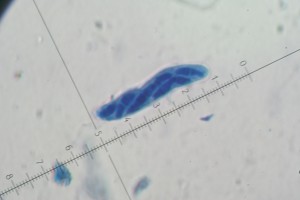
The symptoms caused by this disease can be observed in the leaves of the plants, especially at the edges of the same, where they cause severe burn, this disease is easily distinguishable from others because it shows an annular necrotic lesion in the margins of the leaf hence its name, as the lesion progresses, small black dots (perithecia) form on the leaf, where you can find the ascasporas and ascospores that allow their identification.
The disease can appear at any stage of the crop when the conditions are favorable, and can spread quickly under conditions of humidity and heat, which causes destruction of large amounts of foliage.
Optimum conditions for its development:
- Temperature between 22 to 26 ° C.
- Little rain (Periods of high relative humidity> 85%).
- The release of ascospores occurs in daytime cycles with little rain.
- caricae control.
- Remove as far as possible the leaves infested with the fungus in order to favor ventilation and reduce the risk of presence.
Chemical control
Preventive:
- Application of Phosphorous Acid at a dose of 1.0 L / hectare in irrigation from the third month of the plant, applications of Silicon can be made 4 times every 15 days at a dose of 1.0 liters per hectare sprinkling the foliage.
- Apply contact fungicides such as: Copper hydroxide 2g / L water; Copper oxychloride + Mancozeb 2g / L, chlorothalonil 2 g or mL per liter of water or mancozeb at a dose of 3 gr. per liter of water.
Systemic:
Triazoles: Such as; Diphenoconazole, tebuconazole, fenbuconazole, flutriafol, etc. Applied to the suggested doses that commonly range from 350 to 500 mL per hectare, it can also be used in admixture or alternation with fungicides that especially inhibit breathing Estrobilurinas (azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, fluoxastrobin, etc.) at the recommended doses for each of these.
Note: Applications must be made when the conditions indicated could be favorable for the fungus.
Copyright © All Rights Reserved.
Semillas del Caribe / One Step Ahead